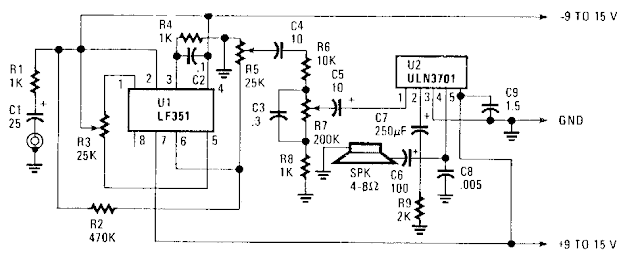
22Watt Car Subwoofer Amplifier
22 Watt Car Subwoofer Amplifier Circuit diagram:

P1_____________10K Log Potentiometer
P2_____________22K Dual gang Linear Potentiometer
R1,R4___________1K 1/4W Resistors
R2,R3,R5,R6____10K 1/4W Resistors
R7,R8_________100K 1/4W Resistors
R9,R10,R13_____47K 1/4W Resistors
R11,R12________15K 1/4W Resistors
R14,R15,R17____47K 1/4W Resistors
R16_____________6K8 1/4W Resistor
R18_____________1K5 1/4W Resistor
C1,C2,C3,C6_____4µ7 25V Electrolytic Capacitors
C4,C5__________68nF 63V Polyester Capacitors
C7_____________33nF 63V Polyester Capacitor
C8,C9_________220µF 25V Electrolytic Capacitors
C10___________470nF 63V Polyester Capacitor
C11___________100nF 63V Polyester Capacitor
C12__________2200µF 25V Electrolytic Capacitor
D1______________LED any color and type
Q1,Q2_________BC547 45V 100mA NPN Transistors
IC1___________TL072 Dual BIFET Op-Amp
IC2_________TDA1516BQ 24W BTL Car Radio Power Amplifier IC
SW1____________DPDT toggle or slide Switch
SW2____________SPST toggle or slide Switch capable of withstanding a current of at least 3A
J1,J2__________RCA audio input sockets
SPKR___________4 Ohm Woofer or two 8 Ohm Woofers wired in parallel
Notes:
- IC2 must be mounted on a suitable finned heatsink
- Due to the long time constant set by R17 and C9 in the dc voltage stabilizer, the whole amplifier will become fully operative about 15 - 30 sec. after switch-on.
Output power (1KHz sinewave):
22W RMS into 4 Ohms at 14.4V supply
Sensitivity:
250mV input for full output
Frequency response:
20Hz to 70Hz -3dB with the cursor of P2 fully rotated towards R12
20Hz to 150Hz -3dB with the cursor of P2 fully rotated towards R11
Total harmonic distortion:
17W RMS: 0.5% 22W RMS: 10%








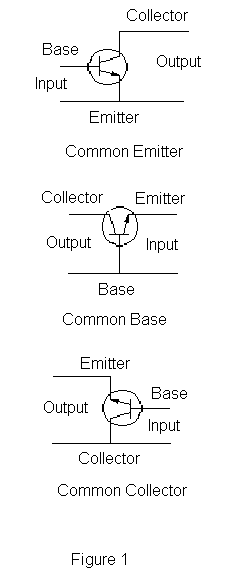












 Amplification of the audio signal is provided by a single stage common emitter amplifier and then via a direct coupled emitter follower. Overall gain is less than 10 but the final emitter follower stage will directly drive 8 ohm headphones. Higher impedance headphones will work equally well. Note the final 2k2 resistor at each output. This removes the dc potential from the 2200u coupling capacitors and prevents any "thump" being heard when headphones are plugged in. The circuit is self biasing and designed to work with any power supply from 6 to 20 Volts DC.
Amplification of the audio signal is provided by a single stage common emitter amplifier and then via a direct coupled emitter follower. Overall gain is less than 10 but the final emitter follower stage will directly drive 8 ohm headphones. Higher impedance headphones will work equally well. Note the final 2k2 resistor at each output. This removes the dc potential from the 2200u coupling capacitors and prevents any "thump" being heard when headphones are plugged in. The circuit is self biasing and designed to work with any power supply from 6 to 20 Volts DC.


